
Pursuing the highly reliable organisation setting, namely the ability to anticipate company’s risks of any kind (commercial, operational, quality-, safety-, security-, health-, and environment-related).
For managers, at any level in the organization, pursuing the highly reliable organisation is not an easy objective to reach: define and assign activities (not simply tasks), control them in a shared way (shared control), it is a complex process that requires a rigorous and original working method.
What’s SHARED KONTROL®
System Logik has conceived and developed SHARED KONTROL®, a method thought for managers responsible of organisational units (from Division to company’s Function, and down to offices and shop floors) to improve the decision making process (because choosen according to the risks brought by the activities managed) and the control of its achievement (because shared with collaborators), thus increasing company’s efficiency.
SHARED KONTROL® is made up of two elements:

la method (the contents)
the enabling infrastructure (the technology)
The 4 inspiring principles
The 4 inspiring principles underlying SHARED KONTROL® are the models esperienced by managers of companies worldwide, namely:

- the organisational system designed on the basis of the High Reliability (High Reliability Organization – HRO), which is the method to work and decide of all orgnisational roles, developed to successfully prevent unexpected risks of major economic impact;
- the decision making based on risks brought by activities (Risk-Based Decision Making – RBDM), which allow the decision maker to oganise and decide about the activities managed, from strategic to operational ones, on the basis of the priority defined by the risk associated to them, thus guaranteeing the appropriate organisational flexibility and increasing the efficiency of his/her role, of the managed unit, and, ultimately, of the company as a whole (made possible thanks to the enabling technology developed);
- the work orgnised by activities and processes (Activity-Based Management – ABM), which eliminate the coordination costs, (that have no added value, and increase the quality of the decisions and the organisational flexibility;
- the management of activities on the basis of the shared control (Goal Setting Theory – GST), which increase the individual motivation and reduce the costs of the organisational control thanks to continuous sharing, between the controller and the controlled, of the definition of the objectives and the control of their achievement (made possible thanks to the enabling technology developed).
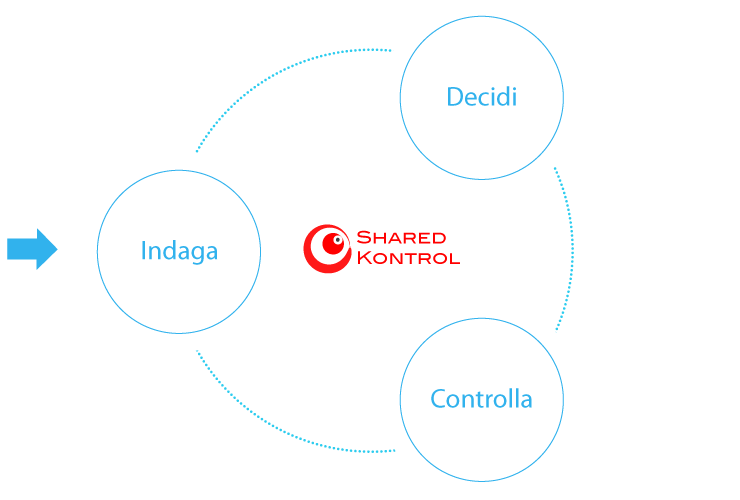
Il modello SHARED KONTROL®
The methodology SHARED KONTROL® reproduces the managerial decision making process: it is focused on 3 interconnected moments:
SHARED KONTROL® and the increase of efficiency
SHARED KONTROL® increases the efficiency thanks to 3 results stemming from its application:

- the increase of the decision-making quality associated with:
- the separation between the moment of decision and that of execution, thus guaranteeing the decision maker the efficient garding of the process;
- the inclusion, in the decision, of company’s risks associated with each activity (not just those of the top management);
- the increase of communiation efficiency stemming from the continuos sharing of information (real-time), as well as from the written and traceable communication amonsgt the actors involved.

- the increase of the working quality associated with:
- the reduction of communication and coordination between controller and the controlled thanks to the use of a unique, dedicated communication means;
- the decrease of conflicts stemming from the clarity (and transparency) and from the increase of the interpersonal communication efficacy;
- the reduction of opportunistic bahaviours and the reinforce of those expected by the controlled thanks to the traceability (and share) of all exchanged communcations.

- the reduction of the costs of analysis, planning and control of the organisational processes stemming from privileging the activity as central unit of work and its design as:
- it is the most stable element in the working situations (with respect to the working processes and organsational units);
- it is expressed in simple terms (not specialised) chosen by the controller and the controlled, thus understandable by all organisational actors;
- traduces operationally the organisational strategies and decisions into “qho should do what, when and how” and thus it facilitates the control and the adaption to organsational changes.
The advantages of SHARED KONTROL®
The advantages of SHARED KONTROL® for those who have to decide regarding the activities of collaborators and the managed organisational unit are as follows:

- enable, those with managerial responsibility and those who have to perform the activities, to decide on the basis of risks associated with the activities to perform, thus avoiding of concentrating the efforts in objectivies and activities of minor economic relevance;
- integrates the activities and the individual responsibilities with the collective ones of the working group and the organitional units of membership, guaranteeing the coherence of objectives of the managed unit;
- ensures the quick and continuous sharing of information necessary for the decision making process based on risks of the organisational actors involved (who is reponsible for the control and who is subject to it);
- makes clear the understanding of the work to perform (“who has to do what, how, by when and with which priority) and foster the estimate of timing and costs of wach activity, as well as, thorugh the bottom up aggregation, the cost of the process in which the activity is included;
- implements quickly and simply the adaptation to organisational changes (without costs of software reconfiguration), guaranteeing continuity in the peformance and control of activities.
Typical processes of application of SHARED KONTROL®
SHARED KONTROL® is largely applicable in all organisatioanal units thanks to the two design criteria: scalability and extendability.
Thanks to the scalability the increase of the persons involved in the application of SHARED KONTROL® (e.g., from the plant to the coporate) does not imply further costs of adaptation or redesign but only infrastructural costs (system’s memory and elaboration speed) significantly less than proportional with the number of new people involved.
The extendability allows to apply SHARED KONTROL® to all working processes that imply the definition of working plans and their control such as:
- internal control (auditing) between the audit service and the audited units;
- management of the sales force betweeen the Network Management and the sales points;
- preventive maintenance between the Maintenance service and the subcontractors (if any) and between the Maintenance service and the production units;
- production planning between the Top Management and the unit or plant managers;
- management by objective or budgeting activities between the supervisor and the staff in the entire company;
- management of the relationship with the providers by the Procurement service;
- management of the HSSE plan by the HSSE Department.